How Does eCommerce Fulfilment Work? A Complete Guide for UK Brands
Every online order follows the same basic journey. A customer clicks “buy,” and somewhere, a product needs to move from a shelf to their doorstep. The process that makes this happen is called eCommerce fulfilment.
On the surface, it sounds straightforward. In practice, fulfilment involves multiple stages, systems, and decisions that directly affect delivery speed, cost, and customer satisfaction. Research shows that 85% of consumers will not shop with a retailer again after a poor delivery experience. For online businesses, getting fulfilment right is not optional.
This guide explains how the eCommerce fulfilment process works, the different models available, and what to consider when choosing a fulfilment approach. It covers everything from goods arriving at a warehouse through to returns landing back at the door.
What Is eCommerce Fulfilment?
eCommerce fulfilment covers everything involved in getting online orders to customers. This includes receiving stock, storing products, picking and packing orders, shipping parcels, and handling returns.
The process applies to both direct-to-consumer (DTC) orders and business-to-business (B2B) shipments. Some brands manage fulfilment themselves, while others outsource to a third-party logistics provider, commonly known as a 3PL.
For brands shipping more than 500 orders per month, the fulfilment model chosen can significantly affect operating costs, delivery times, and the overall customer experience.
The eCommerce Fulfilment Process Step by Step
The fulfilment journey has seven core stages. Each one needs to run smoothly for orders to reach customers on time and in good condition.
1. Receiving and Goods-In
Stock arrives at the fulfilment centre from suppliers or manufacturers. The goods-in team checks the delivery against purchase orders, confirming quantities and inspecting items for damage.
Products are then logged into a warehouse management system (WMS). Any discrepancies or damaged goods are flagged immediately.
Why this stage matters: Errors at goods-in cascade through the entire fulfilment process. Inaccurate stock counts lead to overselling, while undetected damage results in complaints and returns.
Key activities at this stage:
- Unloading deliveries and checking quantities against purchase orders
- Inspecting items for damage or defects
- Logging stock into the WMS with SKU details
- Notifying the brand of any issues
2. Inventory Storage and Management
Once received, products are assigned storage locations within the warehouse. Placement is typically based on product size, turnover rate, and picking efficiency. Fast-moving items are stored in easily accessible locations to speed up order processing.
The WMS tracks stock levels in real time and integrates with eCommerce platforms such as Shopify, Amazon, WooCommerce, and eBay. This keeps inventory synced across all sales channels and prevents overselling.
Core inventory management functions:
| Function | Purpose |
| Real-time stock tracking | Prevents overselling and stockouts |
| Multi-channel sync | Keeps inventory accurate across all platforms |
| Reorder alerts | Flags when stock levels fall below set thresholds |
| Location assignment | Organises products for efficient picking |
| Flexible storage | Allows scaling up or down based on demand |
3. Order Processing
The moment a customer places an order, details are automatically sent to the WMS. The system verifies the order, checks stock availability, and queues it for picking.
Speed at this stage sets the tone for the rest of the fulfilment process. Many fulfilment providers work to same-day dispatch targets, processing orders placed before a set cut-off time for shipment that day.
4. Picking
Warehouse staff locate and retrieve the ordered items from their storage locations. The WMS generates a pick list that guides pickers to the right shelves.
Common picking methods:
- Discrete picking – One order picked at a time, start to finish. Simple but slower for high volumes.
- Batch picking – Multiple orders picked in a single trip. Reduces travel time across the warehouse.
- Zone picking – Pickers are assigned to specific warehouse zones. Items are passed between zones until complete.
- Wave picking – Orders are grouped and picked in scheduled waves, often aligned with courier collection times.
Accuracy at this stage is critical. Mispicks lead to incorrect orders, customer complaints, returns, and additional shipping costs.
5. Packing
Picked items move to a packing station where they are prepared for shipment. Packers select appropriate packaging based on product size and fragility, aiming to protect items while minimising dimensional weight.
For DTC brands, both picking and packing are also a branding opportunity. Custom boxes, tissue paper, thank-you cards, and promotional inserts can all be included at this stage.
Packing considerations:
- Right-sized packaging to reduce shipping costs and waste
- Protective materials for fragile items
- Branded packaging and custom inserts for DTC orders
- Sustainable packaging options, such as recyclable materials and reduced void fill
6. Shipping and Delivery
Packed orders are labelled and handed over to courier partners. Carrier selection depends on destination, delivery speed, cost, and service level requirements.
Most fulfilment providers work with multiple carriers, allowing them to select the best option for each shipment. Real-time tracking information is generated and shared with customers.
Shipping considerations for UK brands:
| Factor | Consideration |
| UK mainland delivery | Next-day options widely expected |
| Scottish Highlands and Islands | May require longer transit times or additional fees |
| EU shipping | Post-Brexit, customs documentation and duties apply |
| International shipping | Carrier selection, customs clearance, and longer lead times |
For brands selling into the EU, using a fulfilment centre within the EU (such as the Netherlands) can simplify customs, reduce delivery times, and improve the customer experience for European buyers.
7. Returns Management
Returns are a standard part of eCommerce fulfilment, not an afterthought. In the UK, approximately £27 billion worth of products are returned each year. January sees a significant spike in returns volume, with some retailers experiencing double their normal return rates after the Christmas period.
Efficient returns processing involves receiving returned items, inspecting them for condition, restocking where appropriate, and disposing of or recycling unsellable goods.
A typical returns process:
- Customer initiates return (online portal or returns label)
- Item arrives back at the fulfilment centre
- Goods-in team receives and logs the return
- Product is inspected for condition
- Decision made: restock, refurbish, recycle, or dispose
- Refund or exchange processed
- Data captured on return reason
Return data is valuable. Tracking why customers return products can highlight issues with sizing, product descriptions, or quality, helping brands reduce future return rates.

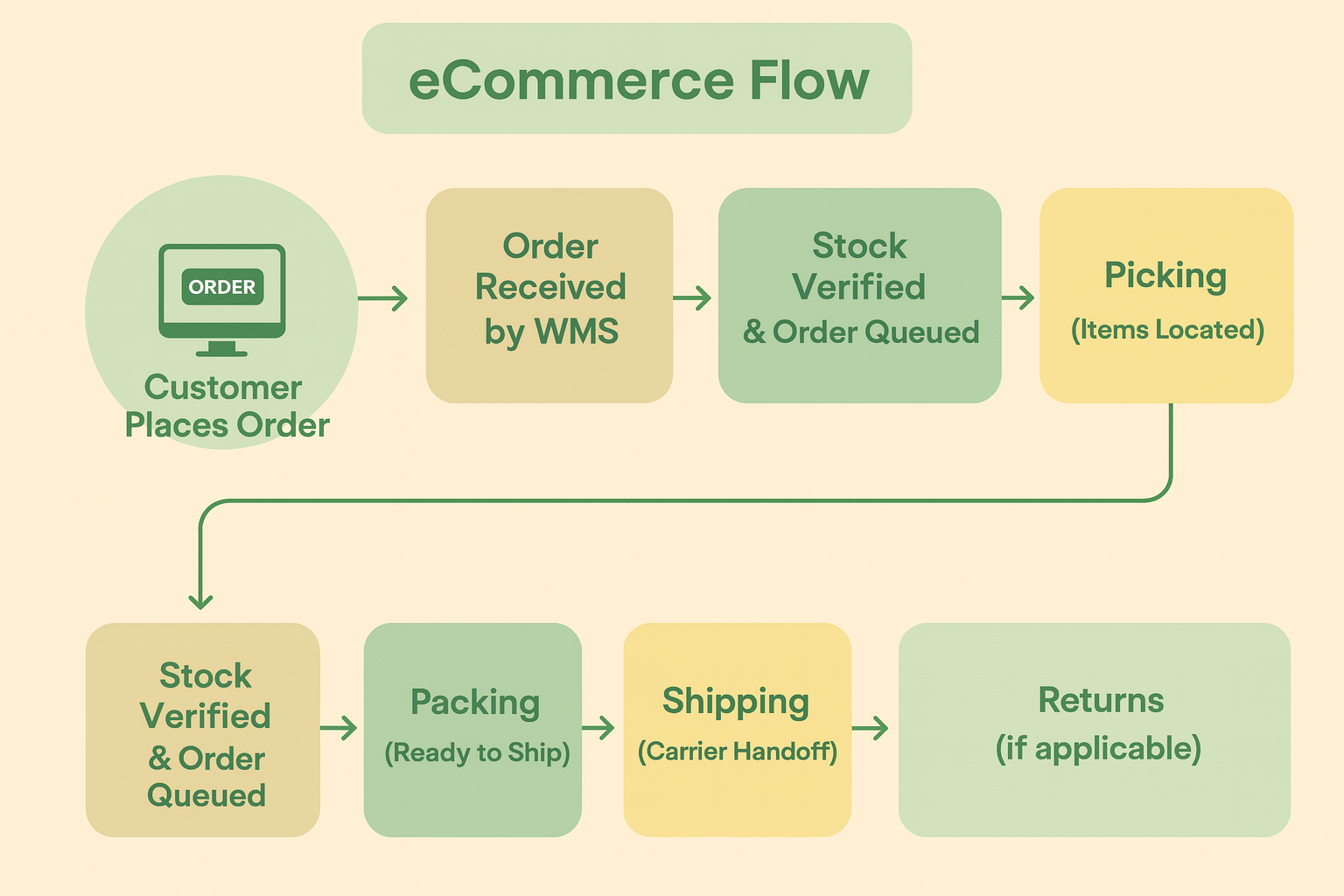
eCommerce Fulfilment Process Flow
The diagram below shows how an order moves through each stage of the fulfilment process.
Types of eCommerce Fulfilment Models
There is no single right way to handle fulfilment. The best approach depends on order volume, product type, budget, and growth plans.
In-House Fulfilment
In-house fulfilment means managing the entire process internally. The business owns or rents warehouse space, employs staff, and handles picking, packing, and shipping directly.
Advantages:
- Full control over packaging, branding, and quality
- Direct oversight of operations
- No third-party fees
Disadvantages:
- Requires investment in space, technology, and staff
- Difficult to scale during peak periods
- Time-consuming, taking focus away from other business areas
Best suited for: Very small brands processing fewer than 100 orders per month, or businesses with highly customised, hands-on products that require specialist handling.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfilment model where the retailer never holds stock. Orders are forwarded directly to a supplier or manufacturer, who ships products to customers on the retailer’s behalf.
Advantages:
- Low startup costs with no inventory investment
- No warehouse space required
- Flexibility to offer a wide product range
Disadvantages:
- No control over shipping speed or packaging quality
- Lower profit margins
- Brand experience is in someone else’s hands
Best suited for: New businesses testing products or markets, or retailers focused on curation rather than product ownership.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
A 3PL provider handles fulfilment on behalf of the brand. This typically includes warehousing, inventory management, picking, packing, shipping, and returns processing.
Advantages:
- Access to fulfilment expertise and infrastructure
- Scalability to handle growth and seasonal peaks
- Reduced operational burden, freeing time for product development and marketing
- Access to negotiated carrier rates
- Multi-location fulfilment options for faster delivery
Disadvantages:
- Less direct control over day-to-day operations
- Need to find a partner aligned with brand values and standards
Best suited for: Brands shipping 500 or more orders per month that want to scale without investing in warehouse infrastructure and staff.
Industry data suggests that 79% of eCommerce businesses use 3PL providers for order fulfilment.
Fulfilment Model Comparison
| Factor | In-House | Dropshipping | 3PL |
| Control over operations | High | Low | Medium |
| Startup cost | High | Low | Medium |
| Scalability | Limited | High | High |
| Branding and packaging control | High | Low | Medium to High |
| Operational burden | High | Low | Low |
| Best for order volume | Under 100/month | Any | 500+/month |
What to Look for in an eCommerce Fulfilment Partner
Choosing the right 3PL is an important decision. The fulfilment partner becomes an extension of the brand, handling products and interacting (indirectly) with customers. Here are the key factors to evaluate.
Technology and Integrations
The fulfilment provider’s platform should integrate with your sales channels. Look for connections to Shopify, Amazon, WooCommerce, eBay, Magento, and other platforms you use.
Real-time inventory visibility, order tracking, and reporting capabilities are essential for managing stock and understanding performance.
Scalability
Can the provider handle your current order volume and grow with you? Ask about capacity during peak periods such as Black Friday and Christmas. A good 3PL should be able to scale up without compromising on speed or accuracy.
Location and Delivery Speed
Warehouse location affects delivery times and shipping costs. For UK customers, a centrally located UK fulfilment centre enables faster delivery to most addresses.
For brands selling into Europe, an EU-based fulfilment centre (such as one in the Netherlands or Belgium) can reduce delivery times and simplify post-Brexit customs requirements.
Accuracy and Reliability
Ask about pick accuracy rates and same-day dispatch targets. Errors are costly, both financially and in terms of customer trust. Look for providers with strong track records and customer satisfaction scores.
Sustainability Credentials
For brands with environmental commitments, the fulfilment partner should align with those values. Look for certifications such as B Corp, paperless operations, recyclable packaging options, and energy-efficient warehousing.
Over 50% of UK consumers now consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions, and 54% expect eco-friendly delivery options at checkout.
Support and Communication
Dedicated account management and responsive support make a significant difference. Ask how issues are handled, what communication channels are available, and how proactive the team is in flagging problems.
Transparent Pricing
Fulfilment costs typically include storage fees, pick and pack charges, and shipping costs. Look for clear pricing structures with no hidden fees for onboarding, peak season surcharges, or minimum commitments.
How the Green Fulfilment Process Works
Green Fulfilment is a UK-based 3PL provider specialising in sustainable, tech-enabled fulfilment for eCommerce brands. Here is how the process works for brands that partner with Green Fulfilment.
Goods-In
Stock is received at UK fulfilment centres (including locations in Glasgow and Swindon) or the EU centre in Venlo, Netherlands. The team performs quality control checks, confirming quantities and inspecting for damage. Any issues are flagged immediately. All stock movements are controlled by RF scanning technology for accuracy.
Storage
Products are stored securely with 24-hour surveillance. Flexible fulfilment warehouse options allow brands to scale capacity up or down based on seasonal demand, reducing costs during quieter periods.
Inventory Management
The Go Green platform integrates with over 30 eCommerce channels, including Shopify, Amazon, WooCommerce, eBay, and Magento. Brands get a single view of inventory across DTC and B2B orders, with real-time stock updates and reporting.
Pick and Pack
Orders are picked and packed with same-day dispatch targets. Sustainable packaging options include recyclable materials and sugarcane-based mailers. Branded packaging and custom inserts are available for DTC orders.
Shipping
Green Fulfilment works with a network of carriers to offer UK next-day delivery, EU shipping from Venlo, and international delivery to over 225 countries. Delivery routes are optimised to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Returns
Returns are processed quickly, with items inspected, restocked where appropriate, and data fed back to the brand. Fast returns handling keeps stock moving and supports a positive customer experience.
Additional Services
Green Fulfilment also offers kitting and assembly, subscription box fulfilment, and optional customer support services where the team handles enquiries on behalf of the brand.
Key facts about Green Fulfilment:
- B Corp certified
- 95% customer satisfaction rate
- 90%+ staff retention over three years
- UK and EU fulfilment centres
- Paperless dispatch and sustainable packaging options
- Transparent pricing with no hidden fees
Sustainability in eCommerce Fulfilment
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in fulfilment. Consumer expectations are shifting, and brands are looking for ways to reduce the environmental impact of their logistics operations.
Why Sustainability Matters
- Over 50% of UK consumers consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions
- 54% of online shoppers expect eco-friendly delivery options at checkout
- 37% say they would pay more for sustainable shipping
What Sustainable Fulfilment Looks Like
Sustainable fulfilment practices can be implemented across multiple stages of the process.
| Stage | Sustainable Practice |
| Packaging | Recyclable materials, reduced void fill, right-sized boxes |
| Documentation | Paperless dispatch, digital delivery notes |
| Warehousing | Energy-efficient lighting, renewable energy sources |
| Shipping | Optimised delivery routes, consolidated shipments |
| Returns | Refurbishment and resale programmes, responsible disposal |
Certifications and Standards
B Corp certification is one indicator of a company’s commitment to environmental and social standards. For brands with sustainability goals, partnering with a certified 3PL extends those values through the fulfilment chain.
Green Fulfilment is one of few UK 3PLs to hold B Corp certification, with sustainability built into operations rather than treated as an add-on.
Common eCommerce Fulfilment Challenges
Fulfilment is operationally complex, and challenges are common. Here are some of the most frequent issues and how to address them.
Peak Season Pressure
The period from Black Friday through to Christmas puts enormous strain on fulfilment operations. Order volumes spike, warehouse space fills up, and courier networks operate at capacity.
How to manage it:
- Plan inventory levels well in advance
- Confirm capacity with your fulfilment provider before peak
- Set clear delivery expectations with customers
- Consider earlier cut-off dates for guaranteed Christmas delivery
Returns Surge
January is often called “Returnuary” due to the volume of post-Christmas returns. Some retailers see return rates double during this period.
How to manage it:
- Ensure your fulfilment partner has efficient returns processing
- Use returns data to identify product issues
- Communicate return policies clearly to customers
Inventory Accuracy
Stock mismatches cause overselling, stockouts, and customer disappointment. Inaccurate inventory is one of the most common fulfilment problems.
How to manage it:
- Use a WMS with real-time inventory tracking
- Integrate all sales channels to a single inventory view
- Conduct regular stock audits
- Set up automated reorder alerts
Shipping Costs and Speed
Customers expect fast delivery, often for free. Balancing speed with cost is a constant challenge.
How to manage it:
- Work with a fulfilment provider that offers multi-carrier options
- Use strategically located warehouses to reduce shipping distances
- Consider offering tiered shipping options (standard, express, next-day)
- For EU customers, use an EU-based fulfilment centre to avoid cross-border delays
Maintaining Brand Experience
Handing fulfilment to a third party can feel like losing control over the customer experience. Packaging quality, insert accuracy, and presentation all matter.
How to manage it:
- Choose a fulfilment partner that offers branded packaging options
- Provide clear guidelines for packing and presentation
- Request sample shipments to check quality
- Look for a partner with dedicated account management and open communication
Frequently Asked Questions
What does eCommerce fulfilment mean?
eCommerce fulfilment is the process of storing, picking, packing, and shipping orders placed through an online store. It also includes managing inventory and handling returns. Fulfilment can be managed in-house or outsourced to a third-party logistics (3PL) provider.
How long does the fulfilment process take?
Timelines vary depending on the provider and shipping method. Many UK 3PLs offer same-day dispatch for orders placed before a cut-off time, with next-day delivery available for most mainland UK addresses. EU and international shipping typically takes two to five days.
What is a fulfilment centre?
A fulfilment centre is a warehouse facility where products are stored, picked, packed, and shipped to customers. Fulfilment centres are operated by 3PL providers or large retailers and are designed for high-volume, fast-turnaround order processing.
When should I outsource fulfilment to a 3PL?
Most brands consider outsourcing when they reach 500 or more orders per month, when in-house fulfilment becomes a bottleneck, or when they want to scale without investing in warehouse space and staff. Outsourcing frees up time to focus on product development, marketing, and growth.
How much does eCommerce fulfilment cost?
Costs vary based on storage volume, order frequency, packaging requirements, and shipping destinations. Typical charges include storage fees, pick and pack fees, and shipping costs. Look for a 3PL with transparent pricing and no hidden fees for onboarding or peak periods.
Can a 3PL handle returns?
Yes. Most 3PLs offer returns management as part of their service. This includes receiving returned items, inspecting them, restocking where possible, and providing data on return reasons. Efficient returns handling protects margins and supports a positive customer experience.
What is the difference between a 3PL and dropshipping?
A 3PL stores your inventory in their warehouse and handles fulfilment on your behalf. You own the stock and control pricing and branding. Dropshipping means you never hold inventory. Orders are sent directly to a supplier who ships to customers. You have less control over packaging and delivery with dropshipping.