The right warehouse can make or break your eCommerce operation. Beyond providing storage space, your warehouse choice directly impacts delivery speed, fulfilment accuracy, and customer satisfaction. For sustainability-minded brands, it also affects your environmental footprint and operational costs.
This guide breaks down the key warehouse types available to UK eCommerce businesses, helping you understand which option aligns with your growth plans, budget, and values.
What Are the Different Types of Warehouses?
Modern warehousing has moved far beyond simple storage. Today’s facilities handle everything from inventory management to final-mile delivery, with some focusing on speed, others on specialised handling, and many now integrating sustainable practices.
The warehouse you choose shapes your entire fulfilment strategy. A fast-growing subscription box service needs different capabilities than a fashion retailer with seasonal peaks. Understanding these differences helps you make decisions that support both immediate needs and long-term growth. Your warehouse choice also determines how quickly you can scale, how efficiently you process returns, and increasingly, how well you meet environmental goals without compromising service quality.

Essential Warehouse Types Every eCommerce Business Should Know
1. Fulfilment Centres
Fulfilment centres differ from traditional warehouses by offering integrated services beyond storage. They handle order processing, picking, packing, shipping, and returns management through a single operation.
Key features:
- Real-time inventory tracking and management
- Multi-channel order processing capabilities
- Integrated returns handling and restocking
- Technology-driven accuracy and speed
Growth potential: High scalability with automated systems that grow with your business
Cost considerations: Medium investment with strong ROI through reduced errors and faster processing
Best for: High-volume eCommerce operations, subscription services, brands requiring fast turnaround times
Leading UK fulfilment providers often integrate sustainability practices like paperless dispatch and recyclable packaging, helping brands reduce their environmental impact while maintaining operational efficiency.
2. Public Warehouses
Public warehouses offer flexible, short-term storage solutions managed by third-party operators. You rent space as needed, sharing facilities and basic services with other businesses.
Advantages:
- Low upfront investment
- Flexible lease terms
- Shared operational costs
- Quick setup and deployment
Limitations:
- Basic service levels
- Limited customisation options
- Shared resources can affect availability
Growth potential: Medium, depending on available space and provider capacity
Best for: Startups, seasonal businesses, companies with fluctuating inventory levels
Public warehousing works well for testing new markets or managing overflow during peak periods without long-term commitments.
3. Private Warehouses
Private warehouses give you complete control over operations, from warehouse organisation structure to staffing and technology choices. You own or lease the entire facility exclusively.
Benefits:
- Full operational control and customisation
- Dedicated staff and resources
- Brand-specific processes and standards
- Long-term cost predictability
Considerations:
- High capital requirements for setup and maintenance
- Full responsibility for staffing and management
- Fixed costs regardless of seasonal fluctuations
Growth potential: High, with complete control over expansion and modifications
Best for: Large enterprises with consistent high volumes, businesses with specific operational requirements, companies with unique product handling needs
4. Smart Warehouses
Smart warehouses use advanced technology, including robotics, AI, and IoT sensors, to automate operations and provide real-time data insights.
Technology integration includes:
- Automated picking and packing systems
- Real-time inventory tracking
- Predictive analytics for demand planning
- Mobile racking warehouse systems for space optimisation
Prerequisites: Technological proficiency and integration capabilities with existing systems
Cost structure: High initial investment with significant long-term efficiency gains
Growth potential: High, with automation enabling rapid scaling without proportional staff increases
Best for: Tech-driven businesses, high-volume operations requiring accuracy, brands prioritising data-driven decision making
5. Distribution Centres
Distribution centres focus on rapid intake, sorting, and redistribution rather than long-term storage. They function as transit points in your supply chain and are especially helpful to eCommerce businesses in the UK wanting to expand into Europe.
Core functions:
- Fast inventory turnover
- Cross-regional distribution
- Multi-location supply support
- Streamlined order routing
Operational benefits:
- Reduced storage time and costs
- Faster regional distribution
- Support for multiple retail locations
- Improved delivery speed to customers
Growth potential: High for businesses expanding into new geographic markets
Best for: Retail chains, businesses with multiple sales channels, brands expanding across the UK and EU
6. Cross-Docking Warehouses
Cross-docking facilities transfer incoming goods directly to outbound vehicles with minimal storage time. Products arrive, get sorted, and ship out within hours.
Process advantages:
- Reduced storage costs
- Faster delivery times
- Lower handling requirements
- Streamlined logistics coordination
Requirements:
- Precise timing and coordination
- Efficient logistics planning
- Strong supplier relationships
- Reliable transportation networks
Best for: Perishable goods, rapid transit operations, businesses focused on minimising storage time and costs
This approach works particularly well for fresh food retailers and fashion brands with fast-moving inventory.
7. Bonded Warehouses
Bonded warehouses operate under customs authority supervision, allowing you to store imported goods before paying customs duties.
Financial benefits:
- Deferred duty payments until goods sell
- Improved cash flow management
- Reduced upfront import costs
- Flexibility in market timing
Compliance requirements:
- Strict customs regulations
- Detailed record keeping
- Security protocols
- Regular inspections
Best for: Import-export businesses, international expansion, companies managing large import volumes
For UK businesses trading with EU partners post-Brexit, bonded warehouses provide crucial flexibility in managing customs obligations.
8. Reverse Logistics Warehouses
These facilities specialise in processing returned items through inspection, restocking, refurbishing, or recycling operations.
Services typically include:
- Return item inspection and categorisation
- Refurbishment and repackaging
- Inventory restocking processes
- Recycling and disposal coordination
Business impact:
- Reduced return processing costs
- Faster inventory return to sale
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Better sustainability through refurbishment
Growth potential: High, especially for eCommerce businesses with significant return volumes
Best for: Fashion retailers, electronics businesses, any operation with return rates above 10%
Many fulfilment centres now integrate reverse logistics, but dedicated facilities often provide more cost-effective solutions for high-return businesses.
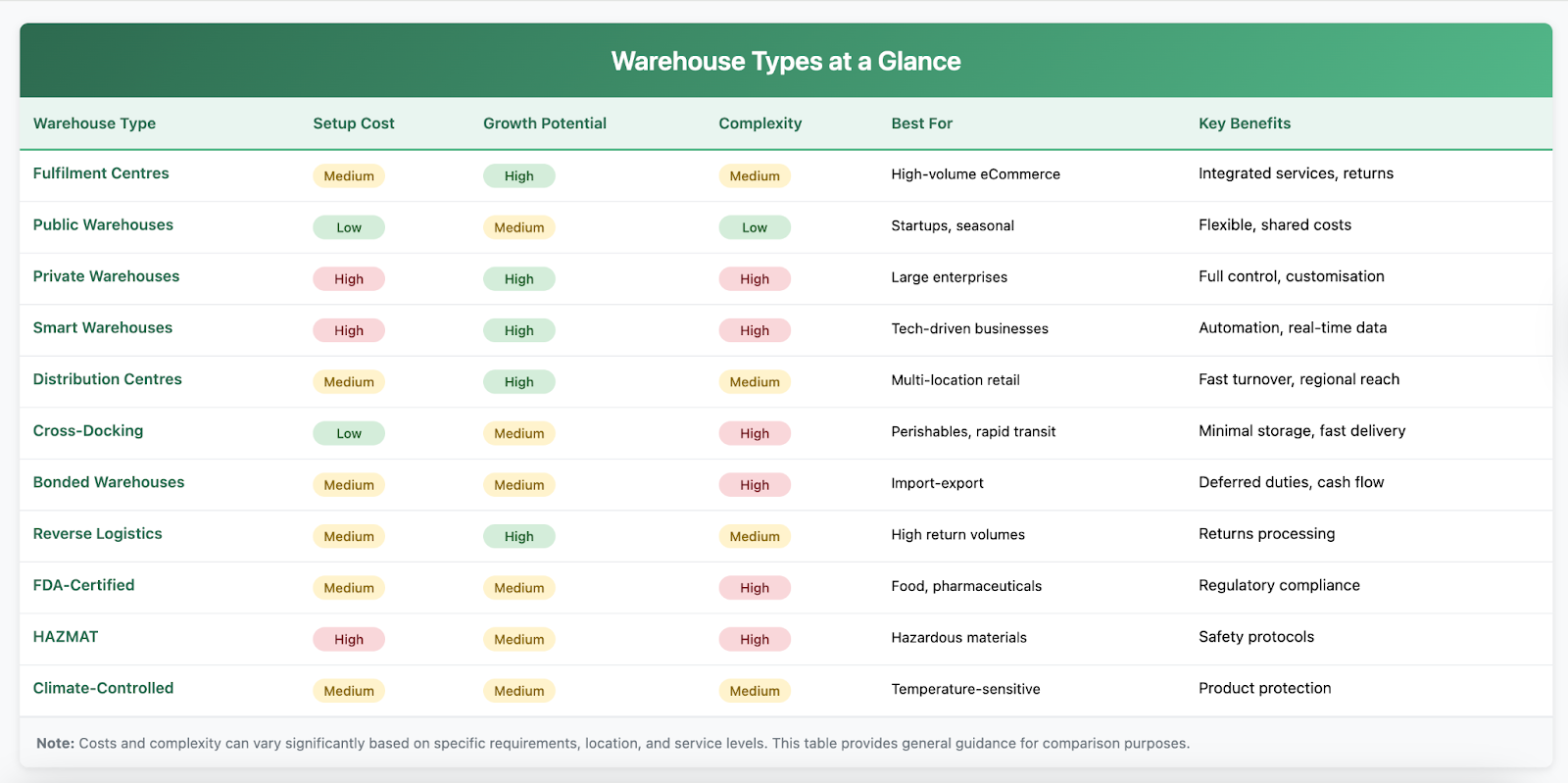
Warehouse Types at a Glance
Specialised Warehouse Solutions for Specific Industries
9. FDA-Certified Warehouses
FDA-certified facilities meet strict standards for storing regulated products, including food, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices.
Compliance features:
- Temperature and humidity controls
- Contamination prevention protocols
- Detailed tracking and documentation
- Regular compliance audits
Required for: Food manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies, medical device retailers, supplement brands
10. HAZMAT Warehouses
Hazardous material warehouses handle products requiring special safety protocols, from industrial chemicals to common household items like aerosols and hand sanitisers.
Safety protocols include:
- Specialised storage systems
- Emergency response procedures
- Staff training and certification
- Environmental protection measures
Applications: Chemical manufacturers, cleaning product retailers, beauty brands with aerosol products
11. Climate-Controlled Facilities
Climate-controlled warehouses maintain specific temperature and humidity conditions for sensitive products.
Energy-efficient options:
- Advanced insulation systems
- Smart climate monitoring
- Renewable energy integration
- Zone-based temperature controls
Suitable for: Food and beverage brands, pharmaceuticals, electronics, certain textiles and cosmeticsProgressive facilities now offer energy-efficient climate control that reduces both operational costs and environmental impact.

How to Choose the Right Warehouse Type for Your Business
Selecting the right warehouse requires evaluating several key factors against your specific business needs and growth plans.
Business Model Alignment
Assess your operational requirements:
- Order volume and seasonal patterns
- Product types and handling requirements
- Geographic reach and delivery expectations
- Growth trajectory and scaling needs
Consider your product characteristics:
- SKU diversity and inventory turnover rates
- Size, weight, and storage requirements
- Special handling or regulatory needs
- Return rates and reverse logistics requirements
Customer-Centric Logistics
Evaluate your customer base:
- Geographic distribution across the UK and EU
- Delivery speed expectations
- Order size and frequency patterns
- Return behaviour and preferences
Delivery performance impact:
- Proximity to major customer clusters
- Integration with preferred shipping carriers
- Weekend and express delivery capabilities
- Returns processing speed and convenience
Scalability and Flexibility
Plan for growth scenarios:
- Projected order volume increases
- New product line introductions
- Geographic expansion plans
- Seasonal capacity requirements
Technology requirements:
- WMS integration with existing platforms
- Real-time reporting and analytics needs
- Multi-channel selling support
- API capabilities for custom integrations
Sustainability Considerations
Environmental impact factors:
- Energy-efficient warehouse operations
- Sustainable packaging options
- Carbon footprint reduction opportunities
- Waste minimisation practices
Business benefits of green logistics:
- Operational cost reductions through efficiency
- Brand reputation strengthening
- Customer loyalty improvements
- Compliance with emerging regulations
According to sustainability-focused fulfilment providers, eco-friendly warehouse practices can reduce operational costs by up to 15% while strengthening brand reputation with environmentally conscious consumers.
Partner Experience and Reliability
Evaluate potential partners:
- Industry experience and track record
- Customer satisfaction rates and testimonials
- Technology capabilities and integration support
- Geographic coverage and expansion plans
Partnership approach:
- Account management and support quality
- Flexibility in service adaptation
- Transparent pricing and reporting
- Long-term strategic alignment
Warehouse Types and Their Impact on Delivery Speed and Costs
Your warehouse choice directly affects both delivery performance and logistics costs, particularly important for UK businesses serving diverse geographic markets.
Location and Proximity Benefits
Strategic positioning advantages:
- Reduced shipping zones and delivery costs
- Faster delivery times to key customer areas
- Lower carbon emissions from shorter transport distances
- Better service levels during peak periods
UK and EU considerations:
- Access to major population centres
- Proximity to shipping hubs and airports
- Cross-border logistics efficiency
- Regional distribution capabilities
Inventory Distribution Strategies
Multi-location benefits:
- Inventory positioning closer to customers
- Risk distribution across facilities
- Seasonal capacity management
- Regional demand optimisation
Technology-enabled distribution:
- Demand forecasting and inventory placement
- Automated stock level optimisation
- Real-time inventory visibility
- Cross-location fulfilment capabilities
Cost-Benefit Analysis Framework
Direct cost factors:
- Storage fees and handling charges
- Shipping costs and delivery speeds
- Technology and integration expenses
- Staff and operational overheads
Indirect benefits:
- Customer satisfaction improvements
- Return processing efficiency
- Brand reputation strengthening
- Operational scalability gains
Real-world data shows that businesses choosing warehouses within 50 miles of their primary customer base can reduce shipping costs by 20-30% while improving delivery speeds significantly.
Sustainable Warehousing: Environmental Considerations by Warehouse Type
Sustainability in warehousing affects both environmental impact and operational costs, making it a crucial consideration for forward-thinking eCommerce businesses.
Energy-Efficient Operations
Sustainable practices across warehouse types:
- LED lighting and smart energy management
- Renewable energy integration
- Efficient heating and cooling systems
- Waste reduction and recycling programmes
Fulfilment centre innovations:
- Paperless dispatch systems
- Recyclable and minimal packaging
- Route optimisation for delivery efficiency
- Electric vehicle integration
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Warehouse location impact:
- Proximity to customers reduces transport emissions
- Access to renewable energy sources
- Public transport links for staff
- Consolidated shipping opportunities
Operational efficiency benefits:
- Reduced waste through better inventory management
- Lower energy costs through efficient systems
- Streamlined processes, reducing resource use
- Technology-driven accuracy reduces returns
UK Sustainability Initiatives
Government support and incentives:
- Grants for energy-efficient warehouse upgrades
- Tax benefits for sustainable logistics practices
- Carbon reduction targets and reporting requirements
- Green transport initiatives and support
Industry trends:
- B Corp certification adoption among logistics providers
- Customer demand for sustainable delivery options
- Retailer requirements for green supply chains
- Insurance benefits for sustainable operations
Leading UK fulfilment providers with B Corp certification report average customer satisfaction rates of 95% while maintaining strong environmental performance, demonstrating that sustainability and service quality work together effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions About Warehouse Types
What’s the difference between a warehouse and a fulfilment centre?
Warehouses provide storage space, while fulfilment centres offer integrated services including picking, packing, shipping, and returns. Fulfilment centres focus on speed and delivery, while warehouses emphasise storage.
How do I determine which warehouse type suits my business size?
Under 500 orders monthly: public warehouses or shared services. 500-5,000 orders: dedicated fulfilment centres. Higher volumes: private warehouses or multiple locations.
What are the cost differences between public and private warehouses?
Public warehouses have lower upfront costs with pay-as-you-use pricing. Private warehouses cost more initially but offer better long-term value for consistent volumes.
Do I need specialised warehousing for international shipping?
Bonded warehouses help with cash flow by deferring customs duties. Evaluate your shipping volume and destinations to determine if specialised facilities are worth the cost.
How does warehouse location affect my shipping costs and delivery times?
Proximity to customers reduces costs by 20-30% and enables next-day delivery. Facilities within 50 miles of your customer base typically perform best.